| Penaeidae (penaeid shrimps) |
| 20.5 cm TL (male/unsexed); 23.5 cm TL (female); max.weight: 35.0 g |
|
benthic; brackish; marine; depth range 0 - 90 m |
| Indo-Pacific: From northeast Africa to south China, Malaysia, Indonesia and north Australia. Introduced in southeast Africa. |
|
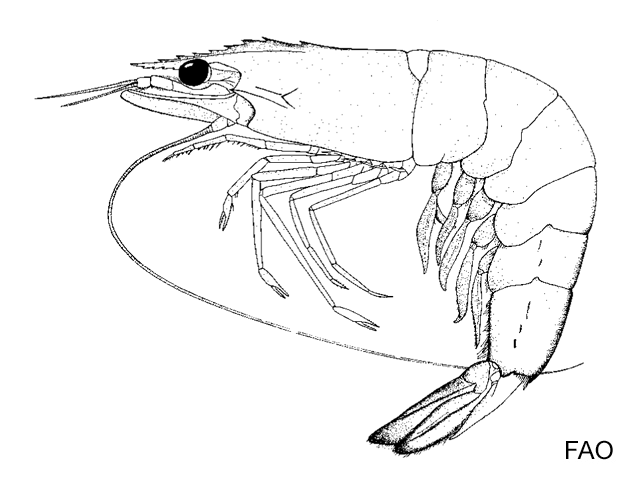
Uniformly glabrous carapace and abdomen. Hepatic and antennal spines on the carapace but no orbital spine. Sigmoidal curved rostrum is armed with 7 or 8 dorsal and 5 or 6 ventral teeth. Telson with no lateral spine. Shallow convexed rostral crest; adrostral carina reaches epigastric teeth; well-defined gastro-orbital carina, which occupies 2/3 distance between hepatic spine and margin of carapace. Color: in life, same as P. merguiensis but slightly more greyish or dull green. Antennal flagellum is yellow or greenish yellow. Posterior half of uropods is yellowish. |
| Minimum depth range based on occurrence (Ref. 110177). To be replaced with a better reference. Juveniles are found in mangrove creek-inlets, intertidal mud flats and far inshore waters (Ref. 121464). Prefers sand or mud bottom and can tolerate high salinity (Ref. 10). Adults live in marine environment and juveniles live in estuarine environment (Ref. 8). |
|
Not Evaluated (N.E.) Ref. 123251)
|
|
|
Source and more info: www.sealifebase.org. For personal, classroom, and other internal use only. Not for publication.