Malacostraca |
Decapoda |
Pandalidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
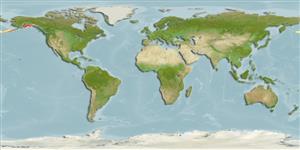
Benthic; depth range 0 - 2648 m (Ref. 91801), usually 45 - 234 m (Ref. 91824). Temperate; 60°N - 27°N, 167°W - 113°W
Eastern Pacific: The west coast of north America from Unalaska Island to Kachemak Bay and Prince William Sound south to Punta Eugenia, Baja California Sur, Mexico.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 30.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 91741); max. published weight: 120.00 g (Ref. 91741); max. reported age: 6 years (Ref. 104007)
"Prawn" of British Columbia, sometimes called the giant shrimp. The body is stout; the carapace covered with a dense short pubescence. The colour of the adults is fawn to red with several distinct white stripes and spots, but the younger individuals show a variety of coloration. Some are green, others brown, while yet others show the red of red algae and
hydroids. This colour change seems to correspond to a change in habitat, for the young specimens live in comparatively shallow water amongst seaweeds and hydroids, while the older individuals go down into deep water. The rostrum is one and a half to one and two thirds times as long as the carapace. There are 14 to 17 dorsal spines extending to the middle of the rostrum, and usually a solitary spine not far behind the acute tip, while the lower limb is armed with 7 or 8 fixed spines.
Maximum depth from Ref. 104449. Maximum common depth from Ref. 104007. Epibenthic (Ref. 91773). Found in bed rocks to muddy sand substrates with adequate shelter for day light hiding (Ref. 91741). Also in crevices on rock faces and in lairs under boulders (Ref. 91824). Nocturnal. Carnivorous and feeds by scavenging on dead animal materials and preying on amphipods, euphausiids, limpets, annelids and other shrimps (Ref. 91741). Preyed upon by fish and octopuses. Also probably eaten by fish such as lingcod, dogfish, and Pacific cod (Ref. 91824). Associated with drift algae, specifically loose kelp (Ref. 91824). Predominantly uses Agarum fimbriatum and Agarum cribrosum kelp beds as nursery habitats (Ref. 91825).
Protandrically hermaphroditic. Initially develops and functions as a male and transforms into females after about 3 to 5 years and remains as female onwards (Ref. 91741). Males become sexually mature when 15 cm TL is reached (Ref. 91750).
Butler, T.H. 2011. (Ref. 91750)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
| FishSource |
Tools
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref.
115969): 4.2 - 6.6, mean 5.3 (based on 121 cells).