Pycnogonida |
Pantopoda |
Callipallenidae
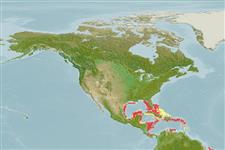
Environment: milieu / climate zone / djupintervall / distribution range
Ekologi
; djupintervall 27 - 55 m (Ref. 2115). Tropical
Western Central Atlantic and Indo-West Pacific.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Könsmognad: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Trunk slender, long; neck very long, with few short spines at insertion of chelifores and proboscis. Cephalic segment longer than posterior 3 segments combined; glabrous lateral processes short, little longer than their diameters. Ocular tubercle low, apex with slender, anterior-pointing tubercle; eyes large. Proboscis short, with setose oral fringe. Abdomen short, erect, with 2 short lateral setae. Chelifores short; scapes with 1 long endal spine, several short ectal spines; chelae palms short, rounded, setose; fingers short, with several teeth. Palps lacking. Oviger long; fourth, fifth segments longest, subequal. Strigilis well developed, with denticulate spines and terminal claw. Legs very long, slender, lightly setose; second tibiae longest; propodus straight, with serrate heel spines matching those of tarsus and second tibia; claw robust; auxiliaries more than half main claw length (Ref. 2115, p. 61-62).
Epibiotic (Ref. 116112).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Könsmognad | Reproduktion | Lek | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Members of the class Pycnogonida are gonochoric and sexually dimorphic. During copulation, male usually suspends itself beneath the female. Fertilization occurs as the eggs leave the female's ovigers. Males brood the egg masses until they hatch. Life cycle: Eggs hatch into protonymphon larva then to adults.
King, P.E. 1973 Pycnogonids. Hutchinson of London. London, UK. 144 p. (Ref. 12)
IUCN Red List Status
(Ref. 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
| FishSource |
Verktyg
Ytterligare information
Trophic EcologyFood items (preys)
Födosammansättning
Födointag
Predatorer
Population dynamicsTillväxt
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Abundans
PhysiologySyreförbrukning
Human RelatedStamps, coins, misc.
Internet-källor
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref.
115969): 21.6 - 27.6, mean 25.5 (based on 36 cells).
Price category
Unknown.